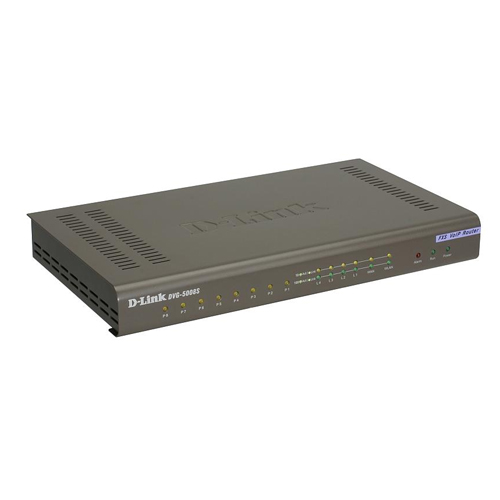
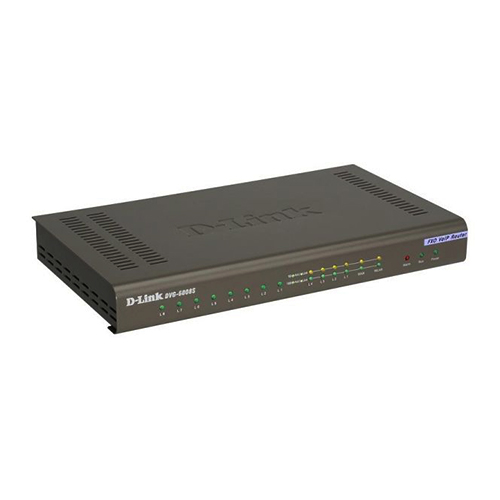
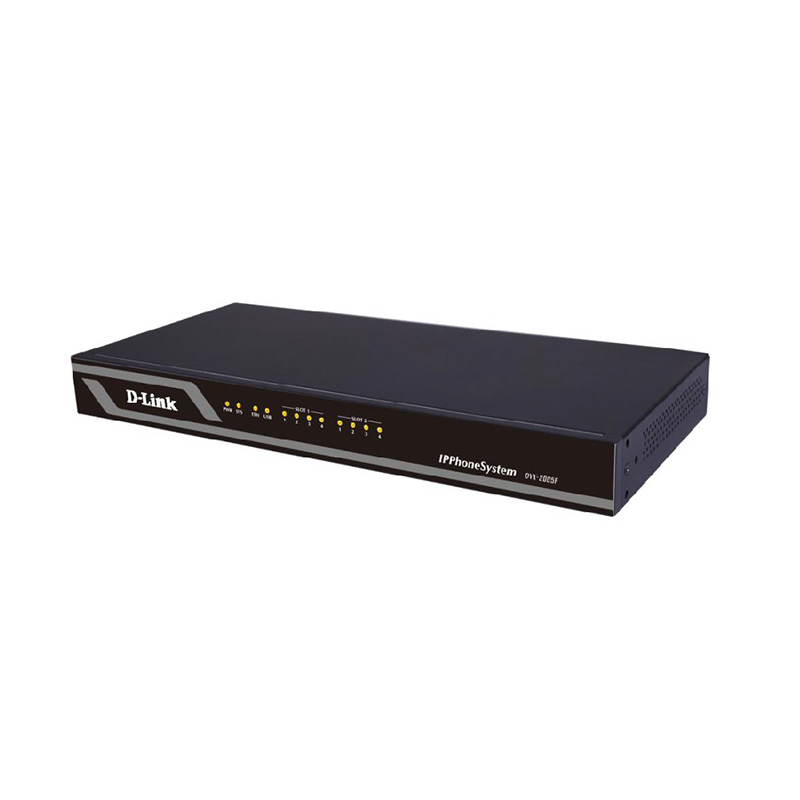
D-Link DVG-5004S 4-Port VoIP Station Gateway Price in Nairobi Kenya.
The DVG-5004S VoIP Station Gateway presents an ideal Internet telephone solution for business use. This gateway converts voice traffc into data packets for transmission over the Internet. It combines the industry’s latest Voice over IP (VoIP) network technology with advanced communication features, and is fully compatible with SIP Internet phone services. By providing both four phone ports and four LAN ports, the DVG-5004S is ideal for equipping up to four workstations with both network and VoIP connectivity through a single device.
Enquire on Whatsapp
SKU:
DVG-5004S
Category: D-link IP phone
Description
Cost Saving and Investment Protection
The DVG-5004S gateway provides businesses with an easy and inexpensive upgrade to Internet telephony while allowing them to retain their existing telephone and fax equipment. This device allows businesses to protect and extend their past investments in telephones, conference speakerphones, and fax machines, and help ease migration to VoIP with a very affordable, incremental investment.
Four Internet Telephone Connections
This gateway provides four FXS ports for simultaneous Internet phone connections. Plug in regular phone sets to these ports and they instantly become Internet telephones. For businesses with a frequent need for long-distance and international phone calls, the VoIP gateway provides great cost savings and convenience while keeping confguration and maintenance to a minimum.
Guaranteed Voice Quality
The DVG-5004S gateway delivers clear voice and reliable phone/fax communication through implementation of internationally recognized standards for voice and data networking. It incorporates Quality of Service (QoS) functions to ensure that audio quality received through the Internet is the same as or even surpasses that received on a standard land line.
Convenient Call Features
The DVG-5004S gateway supports extensive call features such as call waiting and call forwarding, allowing service providers to offer these functions to all subscribers with compatible telephones. Confguration of an individual phone connection is easy using the multi-language Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system or the web-based user interface.
General features
Voice Features
• G.711 a-law 64K
– Packet Interval: 20/30/40/50/60 ms
– Concurrent Calls: 4 ch @ 20 ms
• G.711 μ-law 64K
– Packet Interval: 20/30/40/50/60 ms
– Concurrent Calls: 4 ch @ 20 ms
• G.722 64K
– Packet Interval: 20/30/40/50/60 ms
– Concurrent Calls: 4 ch @ 20 ms
• G.723.1 5.3K/6.3K
– Packet Interval: 30/60/90 ms
– Concurrent Calls: 4 ch @ 30 ms
• G.726 32K
– Packet Interval: 20/30/40/50/60 ms
– Concurrent Calls: 4 ch @ 20 ms
• G.729A/B 8K
– Packet Interval: 20/30/40/50/60 ms
– Concurrent Calls: 4 ch @ 30 ms
• GSM 6.10 Full Rate 13K
– Packet Interval: 20/40/60/80 ms
– Concurrent Calls: 4 ch @ 20 ms
• iLBC 13.3K
– Packet Interval: 30/60/90 ms
– Concurrent Calls: 4 ch @ 30 ms
• DTMF Detection and Generation
• Silence Suppression & Detection
• Comfort Noise Generation (CNG)
• Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
• Echo Cancellation (G.165/G.168)
• Adaptive (Dynamic) Jitter Buffer
• Call Progress Tone Generation
• Auto or Programmable Gain Control
• Built-in Local Mixer
• ITU-T V.152 Voice-band Data over IP Networks
SIP Call Features
• Peer to Peer Call
• Call Hold / Retrieve
• Call Waiting
• Call Pick Up
• Call Park / Retrieve (SIP Server Required)
• Call Forward – unconditional, busy, no answer
• Call Transfer – attended, unattended
• Do Not Disturb
• Speed Dialing
• Repeat Dialing
• Three-way Calling
• MWI (RFC-3842)
• Hot Line and Warm Line
Telephony Specifcations
• In-Band DTMF, Out-of-Band DTMF Relay (RFC2833 or SIP INFO)
• DTMF / PULSE Dial Support
• Caller ID Generation / Detection:
– DTMF
– FSK-Bellcore Type 1 & 2
– FSK-ETSI Type 1 & 2
– FSK-NTT
– FSK: Calling Name, Number, Date and Time, VMWI
• FXS Metering Pulse:
– Polarity Reversal
– 12 kHz calling tone
– 16 kHz calling tone
• T.30 FAX Bypass to G.711, T.38 Real Time FAX Relay
• FXS Line test and diagnostics with visual alarm indication
– Inward self test:
-Loopback – codec
-Loopback – analog
-SLIC DC power voltage
-Tip / Ring DC feed
-Ringer
– Outward Test (GR909 Standard) :
-REN
-Phone Line disconnected
-H.F. DC Voltage (Hazardous and foreign DC Voltage)
-H.F. AC Voltage (Hazardous and foreign AC Voltage)
-Tip / Ring Short
• Modem over IP up to V.34
• ROH Tone (Receiver Off-Hook Tone @ 480 Hz)
• Loop Current Suppression
SIP Account Management
• By Port Registration
• By Device Registration (share account)
• Mixed Mode (Hunt number for inbound, by port number for outbound)
• Invite with Challenge
• Register by SIP Server IP Address or Domain Name
• Support RFC3986 SIP URI Format
SIP Call Management
• Support Outbound Proxy
• Register up to three SIP servers
• SIP Registration Failover Mechanism
• Group Hunting
• Privacy Mechanism / Private Extensions to SIP
• Session Timers (Update / Re-invite)
• DNS SRV Support
• Call Types: Voice / Modem / FAX
• Call Routing by Prefx Number
• User Programmable Dial Plan Support
• CDR Client
• Manual Peer Table (for P2P calls)
• E.164 Numbering, ENUM support
IP Network Specifcations
• Support IPv4, IPv6 future upgradable (Option)
• WAN: Static IP, PPPoE, DHCP, PPTP
• Network Protocol Support:
– IP, TCP, UDP, TFTP, FTP, RTP, RTCP, ARP, RARP, ICMP, NTP, SNTP, SNMP v1/v2, HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, DNS SRV, Telnet, DHCP Server, DHCP Client, STUN Client, UPnP, IGMP snooping, IGMP proxy
• QoS Support:
– WAN: DiffServ, IP Precedence, Priority Queue, Rate Control, 802.1Q (VLAN Tagging), 802.1p (Priority Tag)
– LAN: Rate Limit
• DDNS Support
Network Security Specifcations
• VPN PPTP Client
• DIGEST Authentication
• MD5 Encryption
• DoS Protection
Management
• Web-Based Confguration
• Auto-provisioning (HTTP / HTTPS)
• Telnet
• IVR
• FTP / TFTP / HTTP Software Upgrade
• Confguration Backup and Restore
• Reset to Default Button
• TR-069/104 (Option)
SIP, Voice and FAX Related Standard
• RFC1889 RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications.
• RFC2543 SIP: Session Initiation Protocol
• RFC2833 RTP Payload for DTMF Digits, Telephony Tones and Telephony Signals
• RFC2880 Internet Fax T.30 Feature Mapping
• RFC2976 The SIP INFO Method
• RFC3261 SIP: Session Initiation Protocol
• RFC3262 Reliability of Provisional Responses in Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• RFC3263 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): Locating SIP Servers
• RFC3264 An Offer/Answer Model with Session Description Protocol (SDP)
• RFC3265 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) – Specifc Event Notifcation
• RFC3311 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) UPDATE Method
• RFC3323 A Privacy Mechanism for the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• RFC3325 Private Extensions to the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for Asserted Identity within Trusted Networks
• RFC3362 Real-time Facsimile (T.38) – Image/t38 MIME Sub-type Registration
• RFC3515 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Refer Method
• RFC3550 RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications. July 2003
• RFC3665 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Basic Call Flow Examples
• RFC3824 Using E.164 numbers with the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• RFC3841 Caller Preferences for the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• RFC3842 A Message Summary and Message Waiting Indication Event Package for the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• RFC3891 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) “Replaces” Header
• RFC3892 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Referred By Mechanism
• RFC3960 Early Media and Ringing Tone Generation in the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• RFC3986 Uniform Resource Identifer (URI): Generic Syntax
• RFC4028 Session Timers in the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Draft-ietf-sipping-service-examples-08 for call features
Network Related Standards
• RFC318 Telnet Protocols
• RFC791 Internet Protocol
• RFC792 Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
• RFC793 Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
• RFC768 User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
• RFC826 Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
• RFC959 File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
• RFC1034 Domain Names – concepts and facilities
• RFC1035 Domain Names – implementation and specifcation
• RFC1058 Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
• RFC1157 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
• RFC1305 Network Time Protocol (NTP)
• RFC1321 The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm
• RFC1349 Type of Service in the Internet Protocol Suite
• RFC1350 TFTP Protocol (Revision 2)
• RFC1661 Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
• RFC1738 Uniform Resource Locators (URL)
• RFC2854 The ‘text/html’ Media Type
• RFC2131 Dynamic Host Confguration Protocol (DHCP)
• RFC2136 Dynamic Updates in the Domain Name System (DNS UPDATE)
• RFC2327 SDP: Session Description Protocol
• RFC2474 Defnition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field)
• RFC2516 A Method for Transmitting PPP Over Ethernet
• RFC2616 Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.1
• RFC2617 HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication
• RFC2637 Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
• RFC2766 Network Address Translation – Protocol Translation (NAT-PT)
• RFC2782 A DNS RR for Specifying the location of Services (DNS SRV)
• RFC2818 HTTP Over TLS (HTTPS)
• RFC2916 E.164 Number and DNS
• RFC3022 Traditional IP Network Address Translator
• RFC3489 STUN – Simple Traversal of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) through Network Address Translators (NATs)
Power Adapter
• Input: 100 to 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz
• Output: 12 V, 2 A
Power consumption: 13 W
• MTBF: 458926 hours
Dimensions
• 222 x 145.7 x 33 mm (8.7 x 5.7 x 1.3 inches)
Operating Temperature
• -10 to 40 °C (14 to 104 °F)
Storage Temperature
• -20 to 60 °C (-4 to 140 °F)
Operating Humidity
• 10% to 95% non-condensing
Storage Temperature
• 5% to 95% non-condensing
Certifcations
• FCC Class B
• CE Class B
• CE LVD